Numericals on Current and Dual nature
1) When a steady current flows through a conductor of non uniform cross section which of the quantities remains constant a) Current b) current density c) electric field d) drift speed
a) we know that I=Q/ t so current is independent of area of cross section
b) current density j= I / A ie current density is inversely proportional to area of cross section
c) electric field E = V / l
E=IR / l
a) we know that I=Q/ t so current is independent of area of cross section
b) current density j= I / A ie current density is inversely proportional to area of cross section
c) electric field E = V / l
E=IR / l
E=(Iρl) /Al
E=Iρ / A so E
d) Vd =I / nAe so the drift speed is inversely proportional to area of cross section.
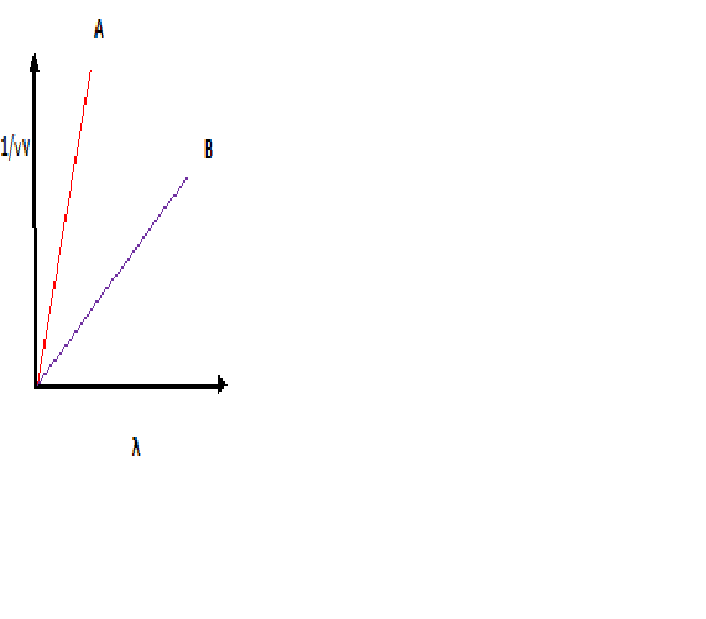
2) The fig shows a plot between 1/√V, where V is the accelarating potential Vs de Broglie wave length λ in the case of two particles having same charge q but different masses m1 and m2 with lines A and B which one will have smaller mass
2) The fig shows a plot between 1/√V, where V is the accelarating potential Vs de Broglie wave length λ in the case of two particles having same charge q but different masses m1 and m2 with lines A and B which one will have smaller mass
λ =h/p =h / (√2mK)
λ=h/(√2mqV)
λ=h/(√2mq)×(1/ √V )
λ=h/(√2mqV)
λ=h/(√2mq)×(1/ √V )
(1/ √V )=(√2mq) /h× λ
The smaller mass is m2
slope of the given graph is (√2mq ) /h
slope of A is more so m1>m2The smaller mass is m2

Comments
Post a Comment