CBSE X
Sai's classes now giving you notes on selected topics (problems with solutions) Intending to support Secondary school students The following topic is on Refraction of light.Click the link below to get notes in pdf format and you can download it.Update will be done at intervals
Sai's Classes (Numericals with solution-Refraction )
CBSE X---Carbon and Its Compounds (Part I )
1) Write down the electronic configuration of carbon?
2) a) What is a covalent bond?
3) Using a bond diagram explain why Nitrogen behaves inert?
4) Why carbon do not form cation or anion while taking part in a reaction?
5) Write down the reasons for the versatility of carbon compounds?
6) Silicon also belong to 14th group like carbon but catenation is not predominant in silicon, justify
7) Why do covalent bonds are otherwise known as molecular bond? Justify with an example
8) Explain the formation of O2 and H2 using electron dot structure.
9) a) What is allotropy?
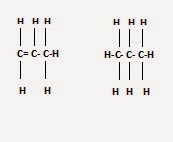
10) Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon, give few examples
11) Name the following hydrocarbons
12) a) What is isomerism?
b) Write the isomers of hexane
13) Draw the structure of a) Benzene b) cyclopentane
14) a) Write down the general formula of alkane, alkene and alkyne
15) a) What are functional groups?
16) a) What is a homologous series?
17) Draw the structure of
18) Write down the IUPAC name of the following
A) B)
19) Write the condensed structure of chloroform, ethyl alcohol, acetylene and acetone
20) Why covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points compare to ionic compounds?
21) Draw the electron dot structure of a) Water b) ammonia
22) How many Single covalent bonds are present in a) pentane b) benzene
23) What are the different structures by which organic compounds can exist?
24) Which major gas is present in Gobar Gas? Draw its electron dot structure
25) What is the condition necessary for the formation of a covalent compound?
CBSE X---Carbon and Its Compounds (Part II )
1) What is Glacial acetic acid?
CBSE X Chemistry(SA1) ACID BASES AND SALTS
- Write one home remedy to reduce acidity
- Name an antacid
- Name the chemical responsible for irritation in Nettle leaf
- Why calamine lotion is applied after an ant bite
- Is ammonium chloride acidic, justify
- pH=5 for a solution what colour change it can produce to methyl orange and phenopthaline
- Why acetic acid is less acidic than HCl?
- Why HNO3 is not used in the preparation of H2 using Zn?
- Why acidified water is used in the electrolysis of water?
- During electrolysis of water if 2 liters of H2 is produced then find the volume of O2 released
- What is Chlor Alkali process?
- What is Margarine?
- What are the uses of chlorine?
- What is a Soda acid fire extinguisher?
- Using anhydrous copper sulphate is it possible to test the presence of moisture, how?
- What is soil reclamation? How it is done?
- Name a salt X which is used in the preparation of Y which is used in bandage , How it is prepared?
- Expand BHC and PVC
- What is hydronium ion?
- Why a milk man add some baking powder in milk during sotrage?
- How is baking powder prepared?
- Name the acid present in apple,tamarind,ant sting.
CBSE X---Carbon and Its Compounds (Part I )
1) Write down the electronic configuration of carbon?
2) a) What is a covalent bond?
b) How it is formed?
c) Give few examples?
3) Using a bond diagram explain why Nitrogen behaves inert?
4) Why carbon do not form cation or anion while taking part in a reaction?
5) Write down the reasons for the versatility of carbon compounds?
6) Silicon also belong to 14th group like carbon but catenation is not predominant in silicon, justify
7) Why do covalent bonds are otherwise known as molecular bond? Justify with an example
8) Explain the formation of O2 and H2 using electron dot structure.
9) a) What is allotropy?
b) what are the allotropes of carbon?
c) Distinguish between the two allotropes of carbon
10) Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon, give few examples
11) Name the following hydrocarbons
12) a) What is isomerism?
b) Write the isomers of hexane
13) Draw the structure of a) Benzene b) cyclopentane
14) a) Write down the general formula of alkane, alkene and alkyne
b) How can you distinguish between the above three
c) Write down the formula of an alkyne which contains 14 hydrogen atoms
d) Write down the formula of any two hydrocarbon which contains carbon and hydrogen in the ratio 1:1
15) a) What are functional groups?
b) Name two functional groups which contains oxygen
c) Name and draw the structure of the functional group present in vinegar and wood spirit
d) Name a functional group which contains C=O
16) a) What is a homologous series?
b) If the molecular mass of the preceding member of two members of homologous series is ‘ N’ u what will be the molecular mass of the succeeding member
c) Write down the first three members of the homologous series of aldehydes , carboxylic acid with their structures
17) Draw the structure of
a) 2,2 dichloro pentane b) 2 chloro 3 methyl hexane c) 2 hexene d) 2 pentanol e) 3 hexanal
18) Write down the IUPAC name of the following
A) B)
19) Write the condensed structure of chloroform, ethyl alcohol, acetylene and acetone
20) Why covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points compare to ionic compounds?
21) Draw the electron dot structure of a) Water b) ammonia
22) How many Single covalent bonds are present in a) pentane b) benzene
23) What are the different structures by which organic compounds can exist?
24) Which major gas is present in Gobar Gas? Draw its electron dot structure
25) What is the condition necessary for the formation of a covalent compound?
CBSE X---Carbon and Its Compounds (Part II )
1) What is Glacial acetic acid?
2) How is vinegar prepared?
3) Show by a chemical reaction ethanoic acid is a monobasic acid
4) Write down the action of sodium carbonate with ethanoic acid
5) What are esters? Name one ester
6) Write down the action of NaOH with esters in acid medium? Name this reaction
7) How can you prepare an alkene from an alcohol ?
8) A compound X which is a by product in anaerobic respiration when treated with sodium yield a compound Y Identify X and Y also write a chemical equation for the same
9) Starting from an alcohol how can you prepare CH3Cl ? Write down all the chemical equation involved in it.
10) What are soaps?
11) Explain the cleaning action of soap?
12) What is a soap micelle? Draw it.
13) What are detergents?
14) What is Hard Water? How it is formed? How can you distinguish it from soft water?
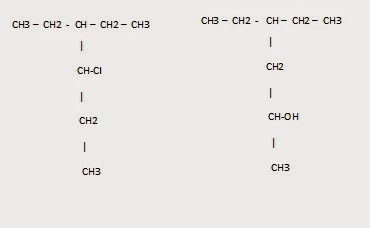
15) How can you distinguish between carboxylic acid and alcohol?
SA1 Chemistry Points to Remember
- During electrolysis of water hydrogen @ cathode and oxygen @ anode (in the ratio 2:1)
- Colour of potassium nitrate is yellow ; nitrogen di oxide is a brown fume formed during thermal decomposition of KNO3
- Gypsum, plaster of paris, blue vitriol(Cu SO4), washing soda have water of crystallization
- Amalgam is a metal in Mercury
- Galvanization coating metal with Zn
- Lustrous non metal is Iodine
- Liquid non metal is Br
- Liquid metal is Hg
- pH is the measure of acidic or basic character of a medium It determines the amount of hydronium ion in the medium
- Oxidation is loss of electron ; reduction is gain
- Electrolysis is a redox reaction
- Na OH is formed from brine solution by Chlor alkali process
- Carbonates and bicarbonates liberate CO2 when treated with an acid
- Very dilute Nitric acid gives hydrogen with Mg and Mn only
- Hydrogen is used in the preparation of Margarine and chlorine in making PVC and CFCs
- Thermit process is a highly exothermic reaction so used for welding railway tracks
- Carbonates ore are clacinated and sulphide ores are roasted to convert the ore to their oxide form
- Electrolytic reduction is used to extract metal high in the activity series
- Cinnabar is the sulphide ore of mercury and Zinc blend that of zinc
- Steel and ornamental gold are alloys
- First step in metallurgy is concentration and last step is refining common to all metals.
- Gaunge is the impurity in the ore
CBSE X Physics(SA1) Short Answer -Electricity
- Name the subatomic particle responsible for electrical conduction in metals
- In a conductor electrons are flowing between two terminals from A to B then find the direction of conventional current
- Name the device used to make and break a circuit
- How many electrons constitute 1 Coulomb charge?
- Write down the SI unit of intensity of current
- 1 mA= __________µA
- Cs-1 is the Unit of ______________ and its SI equivalent is _______________
- Write the SI unit of Potential difference
- Find the work done in moving an electron across a Pd of 1 volt
- What is the use of a rheostat?
- The slope of VI graph gives a physical quantity, name it and write its SI unit
- Unit of resistivity is _________________
- For a given length if the thickness of a wire is increased its resistance _________________ and resistivity ________________________
- Why the overhead power lines are made thick?
- If two resistors are connected in series, if current through one is 2A what is the current through the second?
- Two resistors are connected in parallel, if the Pd between one is 1.5 V what is the Pd across the second?
- What is the SI unit of Power?
- Write down the commercial unit of electrical energy also express it in joule
- Two resistors 3Ω and 5Ω are connected to a battery of 1.6 V first in series and then in parallel in which case the effective resistance greater Justify
- In the above case find the circuit current

information detailed above was great!! please include an article named Student Coaching for NATA in Thrissur it will be awsome...
ReplyDeleteReally helpful post thanks for sharing informative blog, for best CBSE/ ICSE/ IGCSE/IB Coaching in Bangalore click here
ReplyDelete